 A groundbreaking development in the field of science occurred in the early parts of the 20th century when Albert Einstein introduced the theory of relativity to a world that mostly thought that everything in the universe – space and time – are fixed into place. All of these notions about how the universe worked were thrown out of the window as the theory of relativity answered a number of puzzles and problems concerning physics and astronomy that have baffled people in those fields for a long time. Indeed through relativity the existence of black holes and the different observations regarding cosmology began to makes sense to these scientists.
A groundbreaking development in the field of science occurred in the early parts of the 20th century when Albert Einstein introduced the theory of relativity to a world that mostly thought that everything in the universe – space and time – are fixed into place. All of these notions about how the universe worked were thrown out of the window as the theory of relativity answered a number of puzzles and problems concerning physics and astronomy that have baffled people in those fields for a long time. Indeed through relativity the existence of black holes and the different observations regarding cosmology began to makes sense to these scientists.
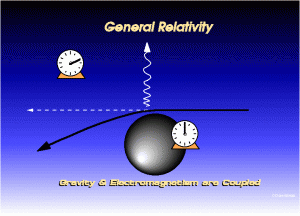
 But what is relativity all about and how was it able to answer these questions? We can begin with what Einstein came up with, the idea that if we are to believe that the natural laws of the universe are absolute and true then they must be true under all circumstances and at all times. According to him, this is only made possible when elements such as space, time, matter, and energy are altered or are changed constantly in order to present us with the same circumstance every time. Applying that to observations of the universe, he supposes that even empty space can contract or expand depending on the position of the person observing it.
But what is relativity all about and how was it able to answer these questions? We can begin with what Einstein came up with, the idea that if we are to believe that the natural laws of the universe are absolute and true then they must be true under all circumstances and at all times. According to him, this is only made possible when elements such as space, time, matter, and energy are altered or are changed constantly in order to present us with the same circumstance every time. Applying that to observations of the universe, he supposes that even empty space can contract or expand depending on the position of the person observing it.
In astronomy, relativity has found its place especially when observing or studying objects that move in a strong gravitational field as well as those that are moving near the speed of light.
