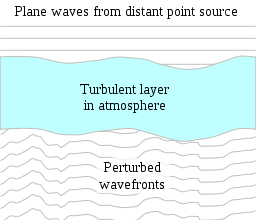
 Astronomical seeing is that blurring and twinkling phenomena of various astronomical objects such as stars, which is naturally caused by the turbulent mixing activities in the Earth’s atmosphere that then varies the optical refractive index. Such conditions on any given night and locations signifies how the Earth’s atmosphere disturbs the images through the telescopes.
Astronomical seeing is that blurring and twinkling phenomena of various astronomical objects such as stars, which is naturally caused by the turbulent mixing activities in the Earth’s atmosphere that then varies the optical refractive index. Such conditions on any given night and locations signifies how the Earth’s atmosphere disturbs the images through the telescopes.
Astronomical seeing is a big concern plaguing Earth-based astronomy. While all those big telescopes boast of their milli-arcsecond resolutions, those real images can never beat up the average seeing disc while on observations. This can denote a factor of up to a hundred between any potential and practical solution. New advances in adaptive optics have been introduced successfully to aid in correcting such effects, improving resolutions of various ground-based telescopes.
Astronomical seeing is known to cause images of all those point sources, just like that of stars to split into different speckle patterns, which can change rapidly through time. Also, lengthy exposure images of the altering speckle patterns automatically results in blurred images of such point sources.
The phenomenon causes the star’s brightness to appear fluctuating. This is a process known to many as scintillation. Another problem concerning Earth-based astronomy and its studies is the rapid movement of fringes in astronomical interferometer.
Its effects were known to be indirectly responsible for some belief that the planet Mars had those infamous canals. When viewing bright objects just like Mars, a still patch of air occasionally comes into view in front that causes some brief moments of clarity. And until the arrival of the charge-coupled devices there were no methods back then to record images at that specific moment. All the observer could do is to remember the image so he can draw it later.
