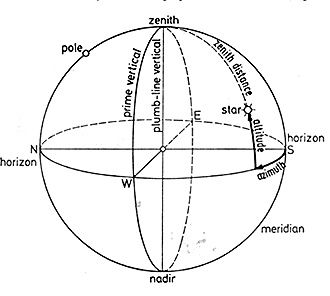
 The celestial sphere is an imaginary surface on which astronomical objects are located. Its center is the center of the Earth. However, the celestial sphere is too large in proportion to Earth’s size making its center considered as the same point of the observer. It is used in describing the location and movement of the stars and other astronomical bodies.
The celestial sphere is an imaginary surface on which astronomical objects are located. Its center is the center of the Earth. However, the celestial sphere is too large in proportion to Earth’s size making its center considered as the same point of the observer. It is used in describing the location and movement of the stars and other astronomical bodies.
The celestial sphere is divided halfway by the celestial equator. Circles of declination are parallel to it. Declination is the distance in angles from north or south of the celestial equator. In order to quantify the directions towards astronomical objects, a celestial coordinate system can be constructed. With this, you can easily locate the Celestial Tropic of Capricorn and the Celestial Tropic of Cancer.
The axis of the Earth from the North Pole when it is extended intersects the celestial sphere in a specific point called the celestial pole. This is near to the North Star called Polaris. This can be of great help in terms of navigation. These celestial spheres rotate from east to west as opposed to the rotation of the Earth in its axis from west to east. This is called the diurnal motion. This is the reason why stars rise in the east, move through the north-south line and set in the west.
Celestial Sphere
